MULTIPLE CLOTTING FACTORS REQUIRED
Clot Generation
Successfully regaining hemostasis during hemorrhage requires a complex balance of factors involved in clot initiation and construction.
Successfully regaining hemostasis during a hemorrhage requires a complex balance of clot initiation and construction.
Healthy Clot Construction
Fibrin creates a mesh around red blood cells and platelets, covering the vessel injury. Activated factor XIII connects and interlaces the fibrin strands, strengthening the clot and providing resistance to plasmin mediated degradation.3
Fibrinogen, factor XIII and von Willebrand factor add the clotting strength needed to achieve stable clot formation and restore hemostasis.
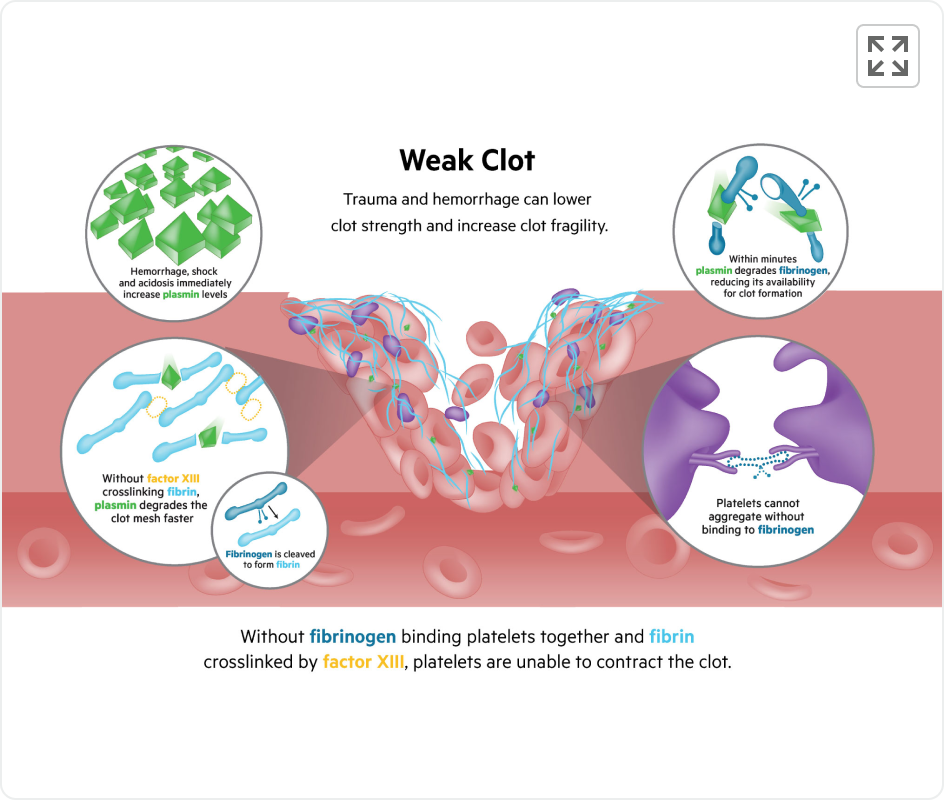
Weak Clot Pathology
Trauma and hemorrhage can lower clot strength and increase clot fragility. In traumatic hemorrhage, fibrinogen, factor XIII,3,4 and platelets are depleted rapidly by a combination of use and plasmin degradation.5
Without fibrinogen binding platelets together and fibrin crosslinked by factor XIII, platelets are unable to contract the clot.
Reduced availability for these factors results in:
- Loose clot formation
- Failure to cover vessel injury
- Rapid clot degradation

INTERCEPT® Fibrinogen Complex
Replenishing these key components is important to stable clot formation and hemostasis.2,6
Be Ready.
When Minutes Matter®
You may also be interested in
References:
- Tanaka KA, Key NS, Levy JH. Blood coagulation: hemostasis and thrombin regulation. Anesthesia and analgesia 2009;108:1433-46.
- Levy JH, Szlam F, Tanaka KA, Sniecienski RM. Fibrinogen and hemostasis: a primary hemostatic target for the management of acquired bleeding. Anesthesia and analgesia 2012;114:261-74.
- Rijken DC, Uitte de Willige S. Inhibition of Fibrinolysis by Coagulation Factor XIII. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:1209676.
- Hiippala ST, Myllyla GJ, Vahtera EM. Hemostatic factors and replacement of major blood loss with plasma-poor red cell concentrates. Anesthesia and analgesia 1995;81:360-5.
- Cushing MM, Asmis LM, Harris RM, et al. Efficacy of a new pathogen-reduced cryoprecipitate stored 5 days after thawing to correct dilutional coagulopathy in vitro. Transfusion 2019.
- Rourke C, Curry N, Khan S, et al. Fibrinogen levels during trauma hemorrhage, response to replacement therapy, and association with patient outcomes. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis : JTH 2012;10:1342-51.